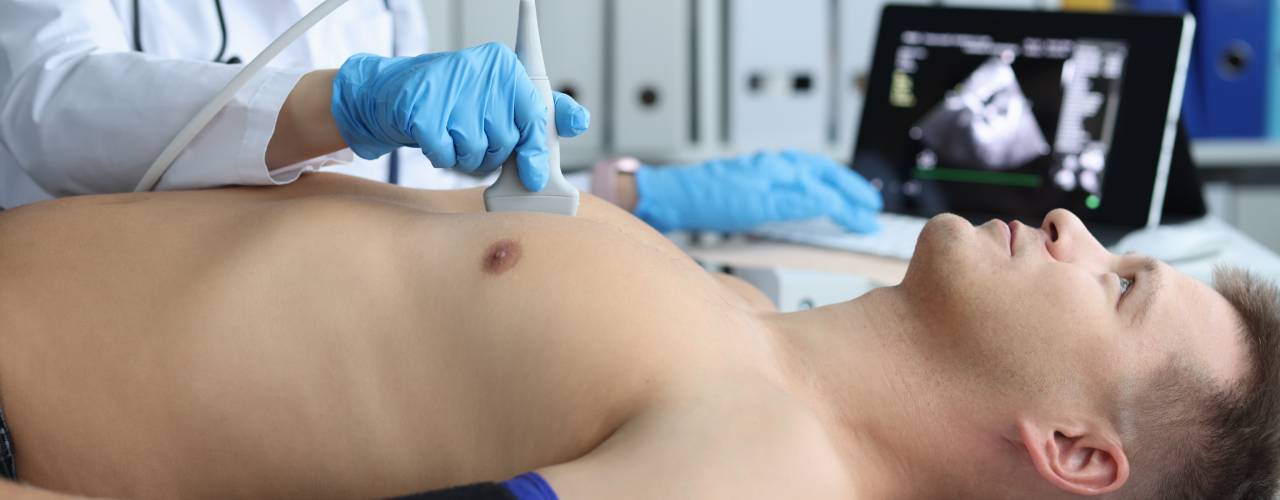
Generally speaking, there’s a lot to know about the use of ultrasounds in cardiology. Most notably, though, understanding the various cardiac ultrasound techniques is crucial for medical professionals. Still, it’s not a bad thing for health-conscious individuals to be educated on. Regardless of whether you’re a professional or a patient, it’s never a bad idea to know more about how accurate and effective heart diagnostics are achieved. In this article, we’ll explore five different types of cardiac ultrasound techniques, comparing their unique attributes, procedures, and specific applications in the medical field.
Transthoracic Echocardiography
Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) is the most common type of cardiac ultrasound. It involves using an ultrasound probe placed on the chest to capture images of the heart. This non-invasive procedure is typically performed with the patient lying down and provides valuable information about the heart’s structure and function. TTE is extensively used to diagnose conditions like heart failure, valve diseases, and congenital heart defects. Due to its simplicity and effectiveness, TTE is often the first-line imaging modality in cardiology.
Transesophageal Echocardiography
Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) offers a more detailed view of the heart compared to TTE. During TEE, a specialized probe is inserted down the esophagus, bringing it closer to the heart. This proximity allows for clearer and more precise images, making TEE particularly useful in assessing conditions that are difficult to evaluate with TTE, such as infections of the heart valves and blood clots in the heart chambers.
Stress Echocardiography
At times, stress echocardiography is required to evaluate how the heart functions under stress. This test can involve physical exercise on a treadmill or stationary bike or the administration of medication that simulates the effects of exercise. Stress echocardiography is instrumental in diagnosing coronary artery disease, as it reveals how well the heart copes with increased workload. By comparing images of the heart at rest and during stress, physicians can detect abnormalities that might not be visible under normal conditions.
3D Echocardiography
3D echocardiography represents a significant advancement over traditional 2D echocardiography. This technology captures three-dimensional images of the heart, providing a more comprehensive and detailed view. The main advantage of 3D echocardiography lies in its ability to offer better visualization of cardiac structures, which is particularly beneficial in planning surgical procedures and assessing complex congenital heart defects. The ability to rotate and view the heart from different angles enhances diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes.
Contrast Echocardiography
The final technique of cardiac ultrasound that we want to compare is contrast echocardiography. This involves the use of contrast agents to improve the quality of ultrasound images. These agents, usually microbubbles, are injected into the bloodstream, where they enhance the reflection of ultrasound waves. This technique is especially useful in patients with poor image quality due to obesity or lung disease. Contrast echocardiography significantly improves the visualization of cardiac chambers and the detection of heart muscle damage, making it an invaluable tool in comprehensive cardiac assessments.